A growing number of governments are pledging to end their contribution to global warming. To stop this global warming every country must come together and put a stop to emitting more greenhouse gas into the air than they can take out.
You must have read in newspapers or magazines or heard some governments or organizations promise to achieve ‘carbon neutrality, to reach ‘net zero emissions’ or to go ‘carbon negative’ by a certain date. Ever wondered what these terms mean? Here is a list of climate terms that can help us what exactly these governments or organizations mean when they promise to reduce global warming.

- Decarbonisation – The process of decreasing the ratio of carbon dioxide or all greenhouse gas emissions that lead to global warming. ‘Full decarbonisation’ is different from decarbonisation as full decarbonisation means making zero carbon emissions, whereas decarbonisation does not imply zero-emission, in decarbonisation the emission of greenhouse gases are balanced by carbon sequestration.
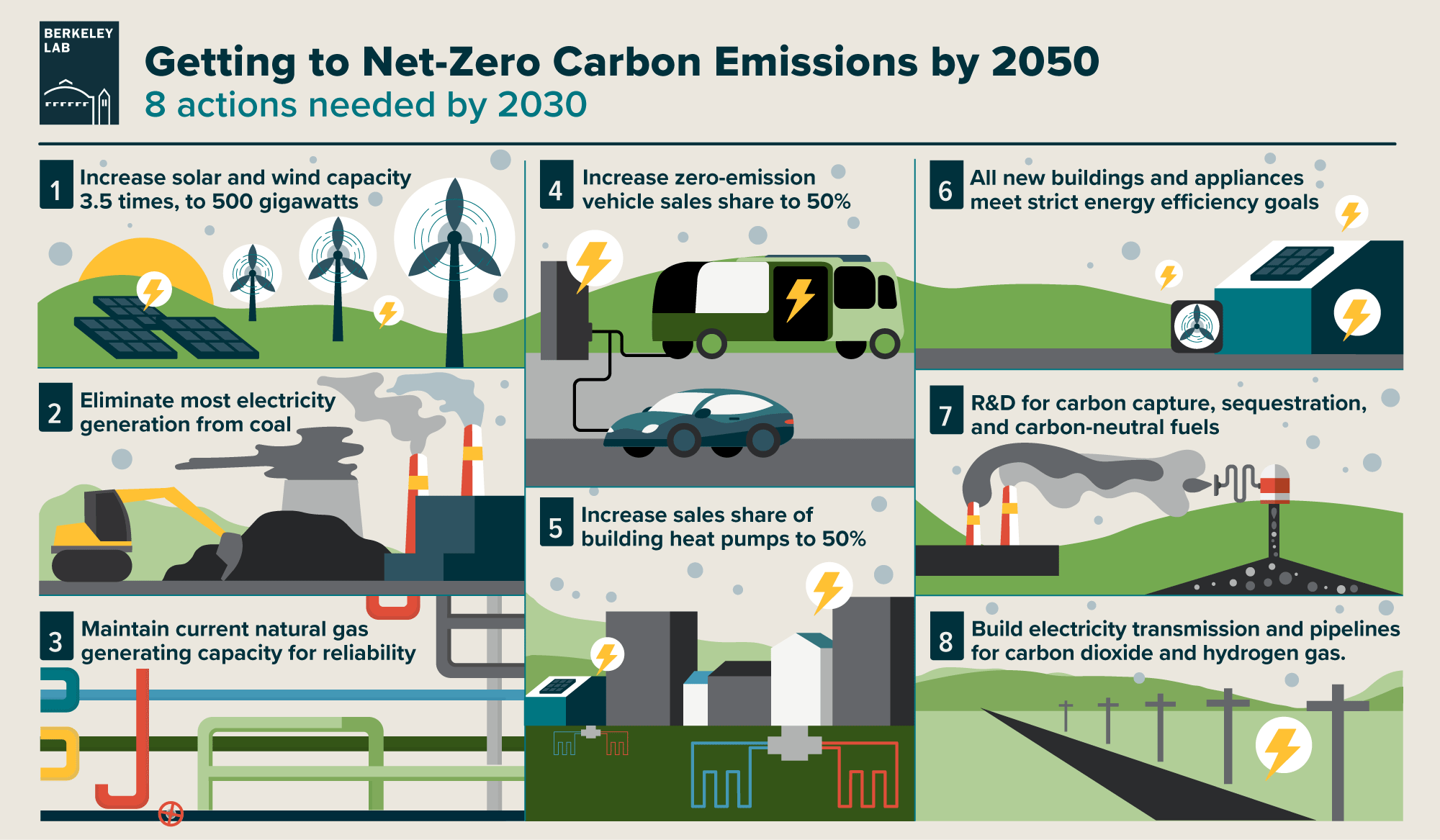
- Net Zero Carbon Emission – This term is often used as a synonym for carbon neutrality. Zero carbon emission refers to having zero carbon emission by a selected date.

- Net Zero GHG Emission – ‘GHG’ stands for greenhouse gas. Net-zero GHG emission happens when all greenhouse gases are balanced by greenhouse gas removals.

- Carbon Neutrality – Carbon Neutrality means balancing between carbon emission and carbon absorption. Another term for it is ‘net zero carbon dioxide emission’

- Climate Neutrality – It means reducing all greenhouse gas emissions as much as possible. This is achieved when greenhouse gas when released into the air is neutralised.